How to Choose the Right Treatment for Oedema and Lymphoedema
Edema affects many individuals, causing swelling in the legs and feet. Oedema and lymphoedema occur when fluid accumulates in tissues. The right treatment for edema is crucial. Effective management can prevent complications. Chronic leg oedema impacts daily life. Obesity often worsens edema. Oedema and lymphoedema require careful attention. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases highlights the importance of understanding these conditions. Choosing the right treatment for oedema and lymphoedema ensures better health outcomes.
Understanding Oedema and Lymphoedema
What is Oedema?
Definition and Symptoms
Oedema refers to swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in the body's tissues. This condition often affects the legs, feet, and ankles. Common symptoms include puffiness, stretched skin, and difficulty moving joints. People may notice indentations when pressing on swollen areas.
Common Causes
Several factors can lead to oedema. Heart failure, kidney disease, and liver cirrhosis are common causes. Medications like steroids and blood pressure drugs may also contribute. Prolonged sitting or standing can cause temporary oedema. Obesity increases the risk of chronic oedema due to added pressure on veins and lymphatic vessels.
What is Lymphoedema?
Definition and Symptoms
Lymphoedema involves swelling from a buildup of lymph fluid. The lymphatic system, responsible for draining excess fluid, becomes compromised. Swelling typically occurs in the arms or legs. Symptoms include heaviness, restricted movement, and thickened skin.
Common Causes
Lymphoedema often results from damage to the lymph nodes or lymphatic vessels. Cancer treatments, such as surgery or radiation, frequently cause this condition. Infections and injuries can also impact the lymph system. Some individuals inherit a predisposition to lymphoedema.
Key Differences Between Oedema and Lymphoedema
Symptoms Comparison
Both oedema and lymphoedema cause swelling, but lymphoedema involves protein-rich lymph fluid. Oedema usually presents with pitting, while lymphoedema often shows non-pitting characteristics. Lymphoedema may lead to skin changes and an increased risk of infection.

Causes and Risk Factors
Oedema arises from fluid retention due to various health issues. Lymphoedema specifically involves the lymphatic system's failure. Obesity plays a significant role in both conditions, exacerbating symptoms and complicating treatment. Lymphoedema frequently follows lymph node removal or damage.
Diagnosing Oedema and Lymphoedema
Medical Evaluation
Physical Examination
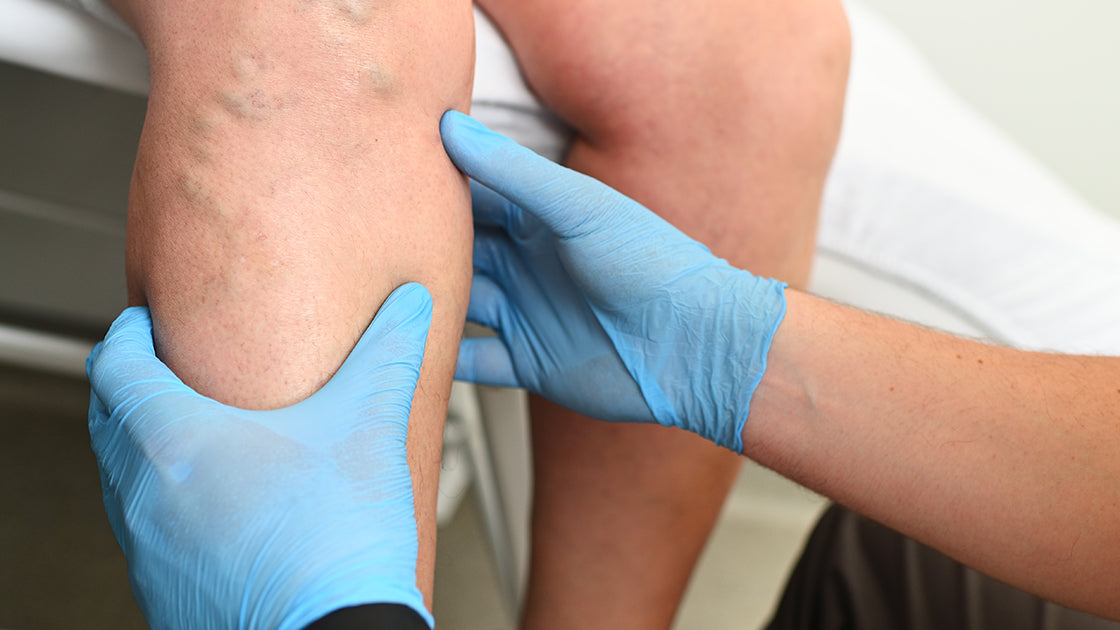
A thorough physical examination plays a crucial role in diagnosing oedema and lymphoedema. Medical providers assess the affected areas for signs of swelling. The examination includes checking for pitting or non-pitting characteristics. Medical providers also evaluate skin texture and color changes. The presence of indentations when pressing on the skin helps identify edema swelling. Observing the body for signs of infection or other complications is essential.
Diagnostic Tests
Medical providers may recommend diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis. Blood tests help rule out underlying conditions like kidney or liver disease. Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, assess the lymphatic system's function. Lymphoscintigraphy provides detailed images of lymph flow. This test offers valuable insights into lymphatic blockages. Accurate diagnosis ensures effective treatment plans.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Impact on Treatment Choices
Accurate diagnosis significantly impacts treatment choices for oedema and lymphoedema. Medical providers tailor treatments based on the severity and cause of the swelling. Proper identification of the disease allows for personalized care. Treatment options range from lifestyle changes to medical interventions. Early detection and intervention improve health outcomes.
Avoiding Misdiagnosis
Avoiding misdiagnosis prevents unnecessary treatments and complications. Misdiagnosis may lead to ineffective therapies and prolonged discomfort. Medical providers must differentiate between oedema and lymphoedema. Clear understanding of the body's response to fluid retention aids in accurate diagnosis. Proper assessment by a medical provider ensures appropriate care and management.
How to Treat Oedema
Lifestyle Changes
Diet and Nutrition
Diet plays a crucial role in managing oedema. Reducing salt intake helps decrease fluid retention. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains supports overall health. Foods high in potassium, such as bananas and spinach, aid in reducing swelling. Monitoring fluid intake prevents excessive fluid buildup. Weight management alleviates pressure on veins and lymphatic vessels.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity enhances circulation and reduces swelling. Walking, swimming, and cycling promote blood flow and lymphatic drainage. Stretching exercises improve flexibility and joint movement. Elevating legs during rest periods decreases fluid accumulation. Light Therapy can complement exercise by reducing inflammation and promoting healing.
Medical Treatments
Medications
Prescription medications may be necessary for severe oedema cases. Diuretics help remove excess fluid from the body. Anticoagulants like Rivaroxaban prevent blood clots that worsen swelling. Medical providers tailor medication plans based on individual needs. Regular monitoring ensures effectiveness and safety.
Compression Therapy
Compression Therapy remains a cornerstone of oedema management. Compression garments, such as stockings or bandages, apply pressure to reduce swelling. Properly fitted garments enhance blood flow and prevent fluid buildup. Medical providers guide patients in selecting appropriate compression levels. Consistent use of compression garments improves outcomes over time.
Alternative Therapies
Herbal Remedies
Herbal remedies offer additional support for managing oedema. Natural diuretics like dandelion and parsley help reduce fluid retention. Herbal teas with ginger or turmeric possess anti-inflammatory properties. Consultation with a healthcare provider ensures safe integration of herbal remedies into treatment plans.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture provides a complementary approach to oedema management. This ancient practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Acupuncture promotes circulation and reduces swelling. Many individuals find relief from symptoms through regular sessions. Light Therapy and Inflammation reduction techniques enhance acupuncture's effectiveness.
How to Treat Lymphoedema
Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT)
Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT) serves as the primary treatment for managing lymphedema. This therapy combines several techniques to reduce swelling and improve lymphatic function.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage
Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD) involves gentle massage techniques. These techniques stimulate the lymphatic system. The goal is to enhance lymph flow and reduce fluid buildup. Trained therapists perform MLD to ensure effectiveness. Regular sessions help maintain lymphatic health.
Compression Bandaging
Compression bandaging follows MLD. Bandages apply pressure to the affected area. This pressure prevents fluid from accumulating. Properly applied bandages support lymphatic drainage. Medical professionals guide patients in using compression bandages effectively.
Surgical Options
Surgical options offer solutions for advanced cases of lymphedema. These procedures aim to restore lymphatic function and reduce excess tissue.
Lymphatic Bypass Surgery
Lymphatic Bypass Surgery creates new pathways for lymph flow. Surgeons connect lymphatic vessels to nearby veins. This connection improves lymph drainage. Patients experience reduced swelling and improved limb function.
Liposuction
Liposuction removes excess fatty tissue. This procedure reduces the volume of the affected limb. Liposuction complements other treatments like CDT. Patients achieve better mobility and comfort.
Self-Care and Management
Self-care plays a vital role in managing lymphedema. Consistent practices enhance treatment outcomes and prevent complications.
Skin Care
Proper skin care prevents infections and maintains skin integrity. Patients should cleanse and moisturize the skin daily. Avoiding cuts and scratches reduces infection risk. Medical providers recommend specific skincare products for sensitive skin.

Exercise and Movement
Exercise and movement support lymphatic health. Activities like walking and swimming promote lymph flow. Regular exercise reduces swelling and improves overall well-being. Red Light Therapy can also aid in reducing inflammation and promoting healing. Patients should incorporate these activities into daily routines.
Choosing the Right Treatment
Factors to Consider
Severity of Condition
The severity of oedema or lymphoedema significantly influences treatment choices. Mild cases may respond well to lifestyle changes and basic interventions. Severe conditions often require comprehensive approaches like Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT). The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in fluid management. A compromised lymphatic system demands more intensive care. MedlinePlus provides valuable insights into understanding these conditions. User awareness about the condition's severity aids in selecting appropriate treatments.
Personal Preferences
Personal preferences impact treatment decisions for oedema and lymphoedema. Some individuals prefer non-invasive methods such as exercise and diet modifications. Others may opt for medical or surgical interventions for quicker results. User comfort with specific treatments ensures adherence to therapy plans. Living with chronic conditions requires considering lifestyle compatibility. Performance Health emphasizes the importance of aligning treatments with personal goals.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Role of Specialists
Specialists play a vital role in managing oedema and lymphoedema. Experts like NHLBI and NIH provide guidelines for effective treatment strategies. User consultations with healthcare professionals ensure accurate diagnosis and tailored care. Specialists assess the lymphatic system to determine the best course of action. MedlinePlus highlights the significance of expert guidance in managing these conditions.
Importance of a Personalized Plan
A personalized treatment plan enhances outcomes for oedema and lymphoedema. User input in developing a plan ensures it meets individual needs. NIAID stresses the value of customized approaches in chronic condition management. Personalized plans consider factors like severity, lifestyle, and preferences. MedlinePlus offers resources for creating effective treatment strategies. A well-structured plan supports long-term health and well-being.
Understanding the differences between oedema and lymphoedema is crucial. Each condition requires specific management strategies. Seeking professional advice ensures effective treatment. Healthcare providers offer guidance tailored to individual needs. Shirley, a patient, found relief through a team of dedicated professionals. Her journey began with a referral to physical therapy. You can achieve similar results by consulting specialists. Managing these conditions effectively involves lifestyle adjustments and medical interventions. Empower yourself with knowledge and support for better health outcomes.
